110.平衡二叉树
力扣题目链接
一棵高度平衡二叉树定义为:一个二叉树每个节点 的左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值不超过1。
求深度适合用前序遍历,而求高度适合用后序遍历。
递归法
这里有个逻辑是如果子树不是平衡二叉树,那么父节点的同样不是平衡二叉树所以直接返回-1就不用继续判断了
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
| class Solution {
public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {
return getHeight(root) != -1;
}
private int getHeight(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
int leftHeight = getHeight(root.left);
if (leftHeight == -1) {
return -1;
}
int rightHeight = getHeight(root.right);
if (rightHeight == -1) {
return -1;
}
if (Math.abs(leftHeight - rightHeight) > 1) {
return -1;
}
return Math.max(leftHeight, rightHeight) + 1;
}
}
|
迭代法
层序遍历并不适合查找树的高度,因为你需要判断到哪个节点,所以可以采取先使用统一递归求深度,再使用迭代求一层一层的判断左右子树
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
| class Solution {
public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return true;
}
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
TreeNode pre = null;
while (root!= null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
while (root != null) {
stack.push(root);
root = root.left;
}
TreeNode inNode = stack.peek();
if (inNode.right == null || inNode.right == pre) {
if (Math.abs(getHeight(inNode.left) - getHeight(inNode.right)) > 1) {
return false;
}
stack.pop();
pre = inNode;
root = null;
} else {
root = inNode.right;
}
}
return true;
}
public int getHeight(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
Deque<TreeNode> deque = new LinkedList<>();
deque.offer(root);
int depth = 0;
while (!deque.isEmpty()) {
int size = deque.size();
depth++;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode poll = deque.poll();
if (poll.left != null) {
deque.offer(poll.left);
}
if (poll.right != null) {
deque.offer(poll.right);
}
}
}
return depth;
}
}
|
257. 二叉树的所有路径
力扣题目链接
这个回溯就有很大的问题,我们知道,回溯和递归是一一对应的,有一个递归,就要有一个回溯,这么写的话相当于把递归和回溯拆开了, 一个在花括号里,一个在花括号外。
所以回溯要和递归永远在一起,世界上最遥远的距离是你在花括号里,而我在花括号外!
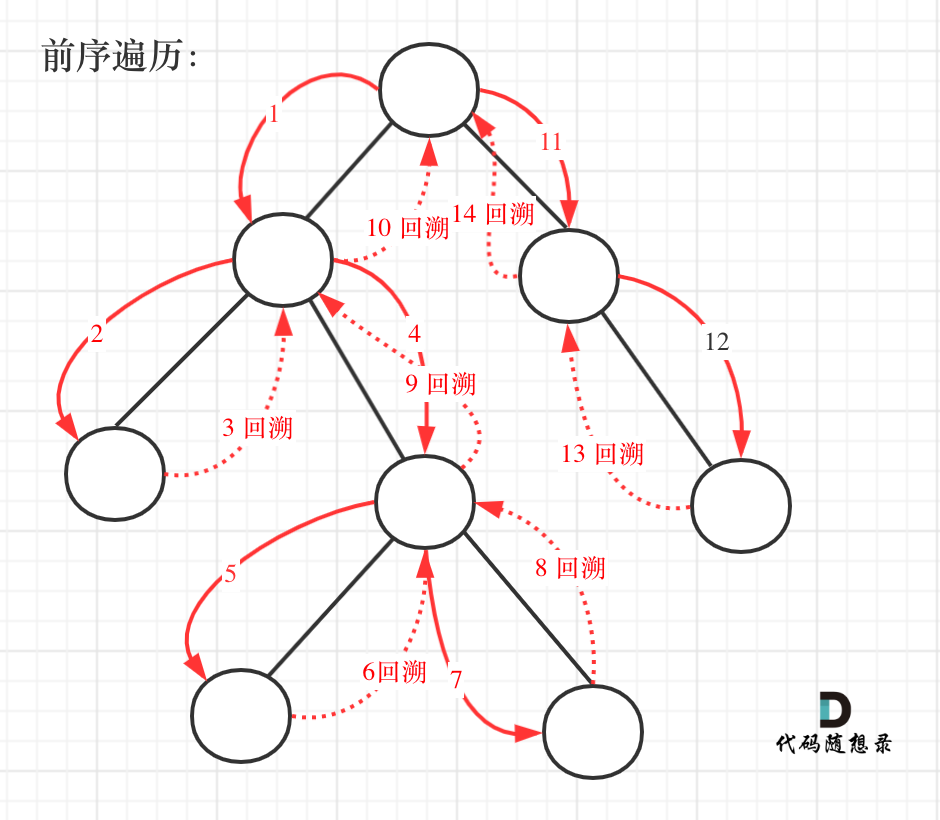
递归
这里回溯的位置是重点。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
| class Solution {
public List<String> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode root) {
List<String> res = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) {
return res;
}
List<Integer> paths = new ArrayList<>();
traversal(root, paths, res);
return res;
}
private void traversal(TreeNode root, List<Integer> paths, List<String> res) {
paths.add(root.val);
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < paths.size() - 1; i++) {
sb.append(paths.get(i)).append("->");
}
sb.append(paths.get(paths.size() - 1));
res.add(sb.toString());
return;
}
if (root.left != null) {
traversal(root.left, paths, res);
paths.remove(paths.size() - 1);
}
if (root.right != null) {
traversal(root.right, paths, res);
paths.remove(paths.size() - 1);
}
}
}
|
迭代法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
| class Solution {
public List<String> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode root) {
List<String> result = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null)
return result;
Stack<Object> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(root);
stack.push(root.val + "");
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
String path = (String) stack.pop();
TreeNode node = (TreeNode) stack.pop();
if (node.left == null && node.right == null) {
result.add(path);
}
if (node.right != null) {
stack.push(node.right);
stack.push(path + "->" + node.right.val);
}
if (node.left != null) {
stack.push(node.left);
stack.push(path + "->" + node.left.val);
}
}
return result;
}
}
|
BFS的迭代和DFS的迭代
BFS和DFS的迭代都是放入然后加入他的子节点而不同的是,DFS的迭代是使用的栈所以每弹出一个节点会接下来弹出的是他的子节点,而BFS弹出的是他们这一行的节点。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
class Solution {
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null){
return result;
}
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
TreeNode cur = root;
while (cur != null || !stack.isEmpty()){
if (cur != null){
stack.push(cur);
cur = cur.left;
}else{
cur = stack.pop();
result.add(cur.val);
cur = cur.right;
}
}
return result;
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
| class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> resList = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
checkFun02(root);
return resList;
}
public void checkFun02(TreeNode node) {
if (node == null) return;
Queue<TreeNode> que = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
que.offer(node);
while (!que.isEmpty()) {
List<Integer> itemList = new ArrayList<Integer>();
int len = que.size();
while (len > 0) {
TreeNode tmpNode = que.poll();
itemList.add(tmpNode.val);
if (tmpNode.left != null) que.offer(tmpNode.left);
if (tmpNode.right != null) que.offer(tmpNode.right);
len--;
}
resList.add(itemList);
}
}
}
|
513.找树左下角的值
力扣题目链接
重要点是区分树的左下角并不是最左边的节点,而是最深长度那一行的最左的节点,所以这个题目用层序遍历来做十分的简答,但是若果用递归的话就要分两步1.求出是否是最深长度,2.求出最左的节点。
回溯方法关联104.二叉树的最大深度
递归
递归三部曲:
确定递归函数的参数和返回值
参数必须有要遍历的树的根节点,还有就是一个int型的变量用来记录最长深度。 这里就不需要返回值了,所以递归函数的返回类型为void。
1
| private void traversal(TreeNode root, int depth)
|
确定终止条件
当遇到叶子节点的时候,就需要统计一下最大的深度了,所以需要遇到叶子节点来更新最大深度。
确定单层递归的逻辑
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
| private void traversal(TreeNode root, int depth) {
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
if (depth > maxDepth) {
maxDepth = depth;
result = root.val;
}
return;
}
if (root.left != null) {
depth++;
traversal(root.left, depth );
depth--;
}
if (root.right != null) {
depth++;
traversal(root.right, depth );
depth--;
}
}
public int findBottomLeftValue(TreeNode root) {
traversal(root, 0);
return result;
}
|
迭代
层序
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| public class Solution {
public int findBottomLeftValue(TreeNode root) {
Deque<TreeNode> queue = new ArrayDeque<>();
queue.add(root);
TreeNode out = new TreeNode() ;
while (!queue.isEmpty()){
int len = queue.size();
out = queue.peek();
while (len>0){
TreeNode temp = queue.poll();
if (temp.left!=null) queue.add(temp.left);
if (temp.right!=null) queue.add(temp.right);
len--;
}
}
return out.val;
}
}
|
