112. 路径总和 力扣题目链接
递归 可以使用深度优先遍历的方式(本题前中后序都可以,无所谓,因为中节点也没有处理逻辑)来遍历二叉树
确定递归函数的参数和返回类型
参数:二叉树的根节点,sum:来计算加上二叉树的一条边之和是否等于是目标和。
再来看返回值,递归函数什么时候需要返回值?什么时候不需要返回值?这里总结如下三点:
如果需要搜索整棵二叉树且不用处理递归返回值,递归函数就不要返回值。(这种情况就是本文下半部分介绍的113.路径总和ii)
如果需要搜索整棵二叉树且需要处理递归返回值,递归函数就需要返回值。 (这种情况我们在236. 二叉树的最近公共祖先 (opens new window) 中介绍)
如果要搜索其中一条符合条件的路径,那么递归一定需要返回值,因为遇到符合条件的路径了就要及时返回。(本题的情况)
106.从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树 力扣题目链接
前序和中序,中序和后序都可以构成二叉树。
来看一下一共分几步:
第一步:如果数组大小为零的话,说明是空节点了。
第二步:如果不为空,那么取后序数组最后一个元素作为节点元素。
第三步:找到后序数组最后一个元素在中序数组的位置,作为切割点
第四步:切割中序数组,切成中序左数组和中序右数组 (顺序别搞反了,一定是先切中序数组)
第五步:切割后序数组,切成后序左数组和后序右数组
第六步:递归处理左区间和右区间
inorder前序,postorder中序
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 class Solution { Map<Integer, Integer> map; public TreeNode buildTree (int [] inorder, int [] postorder) { map = new HashMap <>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < inorder.length; i++) { map.put(inorder[i], i); } return findNode(inorder, 0 , inorder.length, postorder,0 , postorder.length); } public TreeNode findNode (int [] inorder, int inBegin, int inEnd, int [] postorder, int postBegin, int postEnd) { if (inBegin >= inEnd || postBegin >= postEnd) { return null ; } int rootIndex = map.get(postorder[postEnd - 1 ]); TreeNode root = new TreeNode (inorder[rootIndex]); int lenOfLeft = rootIndex - inBegin; root.left = findNode(inorder, inBegin, rootIndex, postorder, postBegin, postBegin + lenOfLeft); root.right = findNode(inorder, rootIndex + 1 , inEnd, postorder, postBegin + lenOfLeft, postEnd - 1 ); return root; } }
654.最大二叉树 力扣题目地址
构造树一般采用的是前序遍历
递归法的三个步骤“确定传入参数和返回类型、确定终止条件、确定单次的内部结构。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 class Solution { public TreeNode constructMaximumBinaryTree (int [] nums) { return constructMaximumBinaryTree1(nums, 0 , nums.length); } public TreeNode constructMaximumBinaryTree1 (int [] nums, int leftIndex, int rightIndex) { if (rightIndex - leftIndex < 1 ) { return null ; } if (rightIndex - leftIndex == 1 ) { return new TreeNode (nums[leftIndex]); } int maxIndex = leftIndex; int maxVal = nums[maxIndex]; for (int i = leftIndex + 1 ; i < rightIndex; i++) { if (nums[i] > maxVal){ maxVal = nums[i]; maxIndex = i; } } TreeNode root = new TreeNode (maxVal); root.left = constructMaximumBinaryTree1(nums, leftIndex, maxIndex); root.right = constructMaximumBinaryTree1(nums, maxIndex + 1 , rightIndex); return root; } }
617.合并二叉树 力扣题目链接
因为不涉及 中节点的处理只有遍历,所以用哪种深度优先的方法都是可以的
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 class Solution { public TreeNode mergeTrees (TreeNode root1, TreeNode root2) { if (root1 == null ) return root2; if (root2 == null ) return root1; root1.val += root2.val; root1.left = mergeTrees(root1.left,root2.left); root1.right = mergeTrees(root1.right,root2.right); return root1; } }
栈迭代
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 class Solution { public TreeNode mergeTrees (TreeNode root1, TreeNode root2) { if (root1 == null ) { return root2; } if (root2 == null ) { return root1; } Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack <>(); stack.push(root2); stack.push(root1); while (!stack.isEmpty()) { TreeNode node1 = stack.pop(); TreeNode node2 = stack.pop(); node1.val += node2.val; if (node2.right != null && node1.right != null ) { stack.push(node2.right); stack.push(node1.right); } else { if (node1.right == null ) { node1.right = node2.right; } } if (node2.left != null && node1.left != null ) { stack.push(node2.left); stack.push(node1.left); } else { if (node1.left == null ) { node1.left = node2.left; } } } return root1; } }
队列迭代
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 class Solution { public TreeNode mergeTrees (TreeNode root1, TreeNode root2) { if (root1 == null ) return root2; if (root2 ==null ) return root1; Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList <>(); queue.offer(root1); queue.offer(root2); while (!queue.isEmpty()) { TreeNode node1 = queue.poll(); TreeNode node2 = queue.poll(); node1.val = node1.val + node2.val; if (node1.left != null && node2.left != null ) { queue.offer(node1.left); queue.offer(node2.left); } if (node1.right != null && node2.right != null ) { queue.offer(node1.right); queue.offer(node2.right); } if (node1.left == null && node2.left != null ) { node1.left = node2.left; } if (node1.right == null && node2.right != null ) { node1.right = node2.right; } } return root1; } }
700.二叉搜索树中的搜索 力扣题目地址
递归很简单不给出代码
迭代
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 class Solution {public : TreeNode* searchBST (TreeNode* root, int val) { while (root != NULL ) { if (root->val > val) root = root->left; else if (root->val < val) root = root->right; else return root; } return NULL ; } };
530.二叉搜索树的最小绝对差 力扣题目链接
计算的是任意两节点的最小值
最简单的方法是二叉搜索树的中序遍历是有序的我们可以计算出数组数组相邻的最小绝对差,当然也可以采用一个双指针,pre记录上一个访问的节点
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 class Solution { TreeNode pre; int result = Integer.MAX_VALUE; public int getMinimumDifference (TreeNode root) { if (root==null )return 0 ; traversal(root); return result; } public void traversal (TreeNode root) { if (root==null )return ; traversal(root.left); if (pre!=null ){ result = Math.min(result,root.val-pre.val); } pre = root; traversal(root.right); } }
这里给出迭代方法层序遍历的迭代方法和深度遍历的迭代方法不同的是,深度遍历每次while只出一个节点,层序遍历每次最外层的while都是获取len然后再次计算循环完一层
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 class Solution { public int getMinimumDifference (TreeNode root) { Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack <>(); TreeNode pre = null ; int result = Integer.MAX_VALUE; if (root != null ) stack.add(root); while (!stack.isEmpty()){ TreeNode curr = stack.peek(); if (curr != null ){ stack.pop(); if (curr.right != null ) stack.add(curr.right); stack.add(curr); stack.add(null ); if (curr.left != null ) stack.add(curr.left); }else { stack.pop(); TreeNode temp = stack.pop(); if (pre != null ) result = Math.min(result, temp.val - pre.val); pre = temp; } } return result; } }
501.二叉搜索树中的众数 力扣题目链接
这个题目要找到出现频率最高的元素
如果不是二叉搜索树,最直观的方法一定是把这个树都遍历了,用map统计频率,把频率排个序,最后取前面高频的元素的集合。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 public class Solution2 { Map<Integer,Integer> res = new HashMap <>(); public int [] findMode(TreeNode root) { int maxFrequency = 0 ; List<Integer> list = new ArrayList <>(); if (root == null ) return list.stream().mapToInt(Integer::intValue).toArray(); travleNode(root); for (Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> entry : res.entrySet()) { int number = entry.getKey(); int frequency = entry.getValue(); if (frequency > maxFrequency) { maxFrequency = frequency; list.clear(); list.add(number); } else if (frequency == maxFrequency) { list.add(number); } } int [] result = list.stream().mapToInt(Integer::intValue).toArray(); return result; } public void travleNode (TreeNode treeNode) { if (treeNode==null )return ; if (treeNode.right!=null ) travleNode(treeNode.right); res.put(treeNode.val, res.getOrDefault(treeNode.val, 0 ) + 1 ); if (treeNode.left!=null ) travleNode(treeNode.left); } }
其次一个关键就是利用搜索二叉树的特性中序遍历是一个有序的,所以再次使用一下之前的pre和cur指针就可以判断有多少个相同了
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 class Solution { ArrayList<Integer> resList; int maxCount; int count; TreeNode pre; public int [] findMode(TreeNode root) { resList = new ArrayList <>(); maxCount = 0 ; count = 0 ; pre = null ; findMode1(root); int [] res = new int [resList.size()]; for (int i = 0 ; i < resList.size(); i++) { res[i] = resList.get(i); } return res; } public void findMode1 (TreeNode root) { if (root == null ) { return ; } findMode1(root.left); int rootValue = root.val; if (pre == null || rootValue != pre.val) { count = 1 ; } else { count++; } if (count > maxCount) { resList.clear(); resList.add(rootValue); maxCount = count; } else if (count == maxCount) { resList.add(rootValue); } pre = root; findMode1(root.right); } }
统一迭代法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 class Solution { public int [] findMode(TreeNode root) { int count = 0 ; int maxCount = 0 ; TreeNode pre = null ; LinkedList<Integer> res = new LinkedList <>(); Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack <>(); if (root != null ) stack.add(root); while (!stack.isEmpty()){ TreeNode curr = stack.peek(); if (curr != null ){ stack.pop(); if (curr.right != null ) stack.add(curr.right); stack.add(curr); stack.add(null ); if (curr.left != null ) stack.add(curr.left); }else { stack.pop(); TreeNode temp = stack.pop(); if (pre == null ) count = 1 ; else if (pre != null && pre.val == temp.val) count++; else count = 1 ; pre = temp; if (count == maxCount) res.add(temp.val); if (count > maxCount){ maxCount = count; res.clear(); res.add(temp.val); } } } int [] result = new int [res.size()]; int i = 0 ; for (int x : res){ result[i] = x; i++; } return result; } }
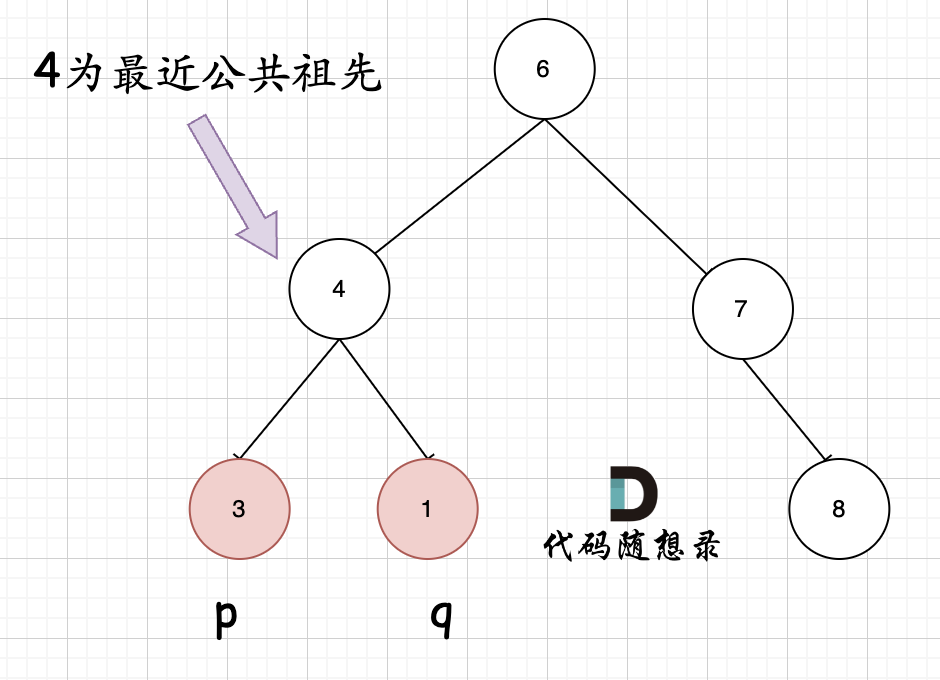
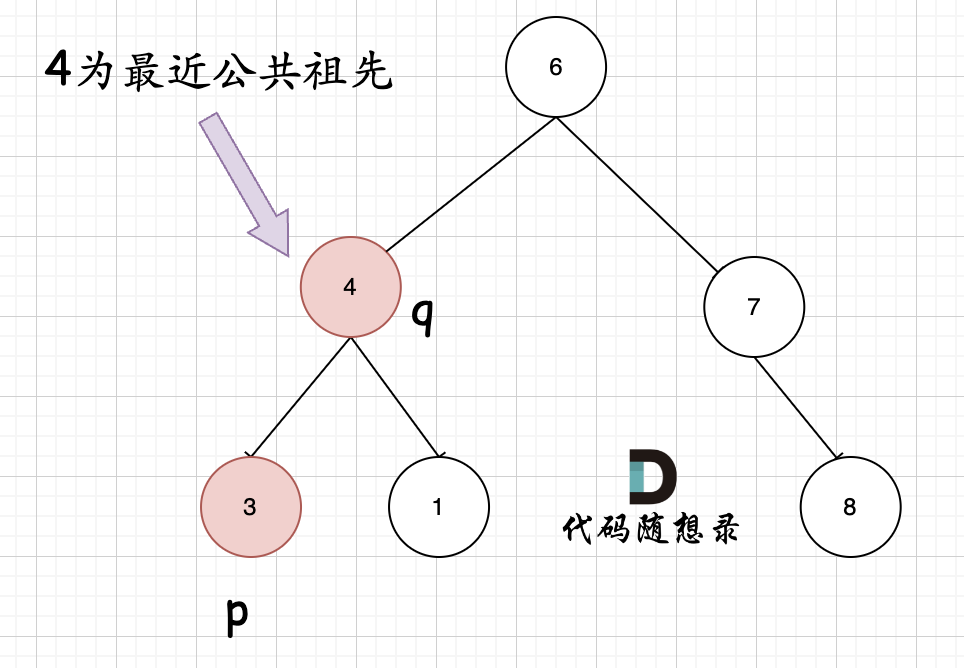
236. 二叉树的最近公共祖先 力扣题目链接
公共祖先一共有两种情况:
判断逻辑是 如果递归遍历遇到q,就将q返回,遇到p 就将p返回,那么如果 左右子树的返回值都不为空 ,说明此时的中节点,一定是q 和p 的最近祖先。
递归三部曲:
确定单次循环
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 TreeNode left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q);TreeNode right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q);if (left == null && right == null ) { return null ; }else if (left == null && right != null ) { return right; }else if (left != null && right == null ) { return left; }else { return root; }
在递归函数有返回值的情况下:如果要搜索一条边,递归函数返回值不为空的时候,立刻返回,如果搜索整个树,直接用一个变量left、right接住返回值,这个left、right后序还有逻辑处理的需要,也就是后序遍历中处理中间节点的逻辑(也是回溯) 。
235. 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先 力扣题目链接
除了可以用二叉树的方法解决还可以利用二叉树的特性
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 class Solution { public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor (TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) { if (root.val > p.val && root.val > q.val) return lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q); if (root.val < p.val && root.val < q.val) return lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q); return root; } }
迭代法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 class Solution { public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor (TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) { while (true ) { if (root.val > p.val && root.val > q.val) { root = root.left; } else if (root.val < p.val && root.val < q.val) { root = root.right; } else { break ; } } return root; } }
701.二叉搜索树中的插入操作 力扣题目链接
这个题目的插入可以随便的插入因为可以直接插入到叶子节点
别忘了这是搜索树,遍历整棵搜索树简直是对搜索树的侮辱。
递归
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 class Solution { public TreeNode insertIntoBST (TreeNode root, int val) { if (root == null ) return new TreeNode (val); TreeNode newRoot = root; TreeNode pre = root; while (root != null ) { pre = root; if (root.val > val) { root = root.left; } else if (root.val < val) { root = root.right; } } if (pre.val > val) { pre.left = new TreeNode (val); } else { pre.right = new TreeNode (val); } return newRoot; } }
迭代
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 class Solution {public : TreeNode* insertIntoBST (TreeNode* root, int val) { if (root == NULL ) { TreeNode* node = new TreeNode (val); return node; } TreeNode* cur = root; TreeNode* parent = root; while (cur != NULL ) { parent = cur; if (cur->val > val) cur = cur->left; else cur = cur->right; } TreeNode* node = new TreeNode (val); if (val < parent->val) parent->left = node; else parent->right = node; return root; } }
450.删除二叉搜索树中的节点 力扣题目链接
删除时遇到的五种情况
有以下五种情况:
第一种情况:没找到删除的节点,遍历到空节点直接返回了
找到删除的节点
第二种情况:左右孩子都为空(叶子节点),直接删除节点, 返回NULL为根节点
第三种情况:删除节点的左孩子为空,右孩子不为空,删除节点,右孩子补位,返回右孩子为根节点
第四种情况:删除节点的右孩子为空,左孩子不为空,删除节点,左孩子补位,返回左孩子为根节点
第五种情况:左右孩子节点都不为空,则将删除节点的左子树头结点(左孩子)放到删除节点的右子树的最左面节点的左孩子上,返回删除节点右孩子为新的根节点。
第五种情况有点难以理解,看下面动画:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 class Solution { public TreeNode deleteNode (TreeNode root, int key) { if (root == null ) return root; if (root.val == key) { if (root.left == null ) { return root.right; } else if (root.right == null ) { return root.left; } else { TreeNode cur = root.right; while (cur.left != null ) { cur = cur.left; } cur.left = root.left; root = root.right; return root; } } if (root.val > key) root.left = deleteNode(root.left, key); if (root.val < key) root.right = deleteNode(root.right, key); return root; } }
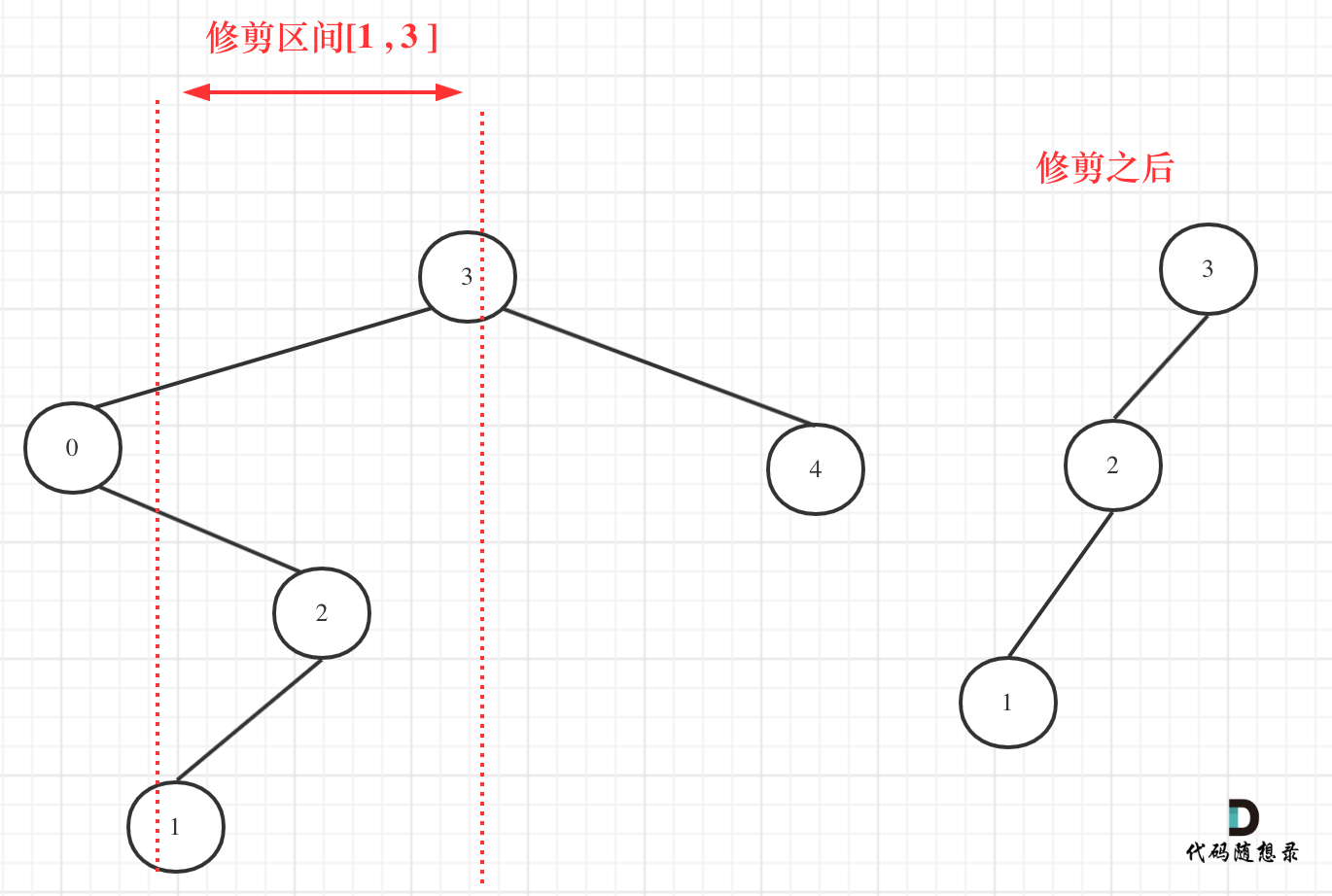
669. 修剪二叉搜索树 力扣题目链接
给定一个二叉搜索树,同时给定最小边界L 和最大边界 R。通过修剪二叉搜索树,使得所有节点的值在[L, R]中 (R>=L) 。你可能需要改变树的根节点,所以结果应当返回修剪好的二叉搜索树的新的根节点。根据下图我们可以得只不能只根据一个节点不在修建区间就把他的子树完全删除。
因为是要遍历整棵树,做修改,其实不需要返回值也可以,我们也可以完成修剪(其实就是从二叉树中移除节点)的操作。
但是有返回值,更方便,可以通过递归函数的返回值来移除节点。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 class Solution { public TreeNode trimBST (TreeNode root, int low, int high) { if (root == null ) { return null ; } if (root.val < low) { return trimBST(root.right, low, high); } if (root.val > high) { return trimBST(root.left, low, high); } root.left = trimBST(root.left, low, high); root.right = trimBST(root.right, low, high); return root; } }
迭代法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 class Solution { public TreeNode trimBST (TreeNode root, int low, int high) { if (root == null ) return null ; while (root != null && (root.val < low || root.val > high)){ if (root.val < low) root = root.right; else root = root.left; } TreeNode curr = root; while (curr != null ){ while (curr.left != null && curr.left.val < low){ curr.left = curr.left.right; } curr = curr.left; } curr = root; while (curr != null ){ while (curr.right != null && curr.right.val > high){ curr.right = curr.right.left; } curr = curr.right; } return root; } }
# 108.将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树力扣题目链接
这个题目的重点是需要转换为平衡的二叉树
因为大家默认都是从数组中间位置取值作为节点元素,一般不会随机取